The BRICS are a group of leading emerging economies. Originally comprising five countries, the BRICS have now expanded to include ten countries: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, the United Arab Emirates and Indonesia.
The BRICS countries are home to 48% of the world’s population and have similar challenges in health care.
The BRICS Health Journal aims to promote medical research, public health and scientific cooperation among the BRICS countries.
In the scope of the BRICS Health Journal:
- Public health
- Health care system
- Medical education
- Infectious diseases
- Noncommunicable diseases
- Digitisation of healthcare
- The global challenge of cancer
- Mental health
- Maternal and child health
- Tuberculosis control
- Advancing the global fight against HIV/Aids
- Antimicrobial resistance
The Journal is issued four times a year and publishes original research articles, review articles and letters to the editor.
Journal target audience
- Scientists and Researchers: Medical professionals, physicians, scientists and researchers from the BRICS countries who are engaged in medical and scientific research and strive to publish their work in a ranked and recognized journal.
- Medical organizations and institutions: Medical centres, hospitals, research institutes and clinics in the BRICS countries that are interested in disseminating their scientific and clinical research.
- Health Authorities and State Institutions: Ministries of Health and other public authorities responsible for health care in the BRICS countries who can use the journal to share experience and information about health care.
- Medical schools: Students of medical and scientific specialties, graduate students and scientific teachers from medical schools of the BRICS countries.
- International organizations and partners: International scientific and medical organizations that are interested in cooperation with scientists and medical specialists from the BRICS countries
Current issue
This policy perspective highlights how the 2025 BRICS chairship, under Brazil’s leadership, advanced a collective health agenda rooted in equity, innovation, and solidarity among Global South nations. Through the XV BRICS Health Ministers’ Meeting (Brasília, 17 June 2025), members prioritized cooperation on tuberculosis, regulatory convergence, digital health, and the elimination of socially determined diseases. These efforts reaffirmed health as a strategic pillar for multilateral renewal. Among the major outcomes, the bloc launched the Partnership for the Elimination of Socially Determined Diseases, the Network of National Public Health Institutes, and progress on regulatory harmonization and artificial intelligence and health data governance. Together, these initiatives created operational frameworks to expand access, strengthen research collaboration, and build technological sovereignty. Brazil’s domestic achievements – such as World Health Organization’s 2024 certification of lymphatic filariasis elimination and the nationwide digital transformation through the SUS Digital Program and the National Health Data Network – reflect how national progress can reinforce collective goals. By translating shared political will into practical cooperation, BRICS demonstrates that South–South collaboration can deliver measurable results. These advances position the bloc as a driving force for inclusive global health governance and a model for how emerging economies can advance universal health coverage and health for all on a planetary scale
Brazil assumed the presidency of BRICS this year and stipulated some health priorities as strengthening BRICS Network of Research in Public Health and Health Systems; strengthening BRICS Vaccine Research and Development Centre; elimination of socially determined diseases and infections; tuberculosis research network; combat public health emergencies of international concern or catastrophes; physical and technological infrastructure for specialized care in remote and hardto-reach areas; BRICS regulatory authorities for medical products; and artificial intelligence and data governance in health systems. BRICS leaders gathered for the 17th Summit on July 6–7 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, where they issued the Rio de Janeiro Declaration, themed “Strengthening Global South Cooperation for More Inclusive and Sustainable Governance”. In the human and social development promotion section of the main document, the health-related paragraphs highlighted two initiatives led by Fiocruz, a strategic institution of the Brazilian State: the BRICS Network of Research in Public Health and Health Systems and the BRICS Vaccine Research and Development Centre. A third initiative, the Conference of the BRICS National Public Health Institutes, coordinated by Fiocruz, although not mentioned at the Leaders’ Summit, earned a place in the BRICS Health Ministers’ declaration due its significance. Its recommendations will help advance knowledge on public health issues and support decision-making processes. The objective of this article is to report the development of initiatives led by Brazil during its presidency in 2025 and subsidize India, the next presidency, to continue the health actions related to health.
This article analyzes the evolving health cooperation between Brazil and China as a strategic frontier in South-South collaboration. At a time of global health insecurity and technological inequality, the partnership between these two continental powers offers a transformative alternative to traditional donor-recipient models. The analysis traces a shift from commodity-based trade to a potential alliance in co-innovation, encompassing vaccines, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and digital health. Brazil’s deep dependency on imported medical inputs and its fragmented industrial base stand in contrast to China’s stateled model of technological scaling and global health outreach. Yet, this asymmetry also reveals opportunities: Brazil’s universal health system, research institutions, and regional leadership can be aligned with China’s production capacity, digital infrastructure, and development finance to build shared technological sovereignty. The paper examines how Brazil’s renewed industrial policy under Lula’s administration opens new pathways for joint research and development, regional pharmaceutical production, and equitable technology transfer. It also confronts persistent challenges – technological imbalances, intellectual property constraints, institutional volatility, and geopolitical pressures aimed at curtailing South-South alignment. A successful partnership, the article argues, must be grounded in transparent governance, mutual benefit, and a commitment to health as a public good. It concludes with a proposal for a decentralized health innovation ecosystem in Brazil, inspired by China’s special economic zones, to overcome the historical concentration of technological power and promote equitable development across the North, Northeast, and Center-West. In doing so, the Brazil–China relationship can become a model for a more just, resilient, and multipolar global health order.
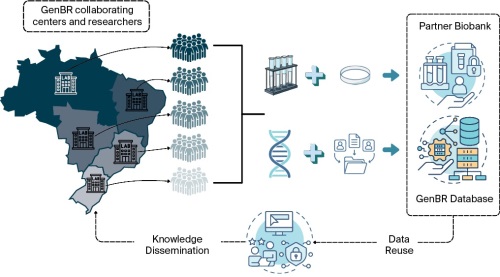
This study aimed to assess the implementation of the Brazilian National Program for Genomics and Precision Public Health (GenBR) over its initial five years, identifying key achievements, challenges, and lessons for integrating genomics into public health systems in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Established by Ministerial Ordinance GM/MS No. 1,949 on August 4, 2020, GenBR aims to lay the foundation for genomics and precision health within Brazil’s Unified Health System. Its primary goals include advancing science and technology countrywide, fostering the development of a national genomics industry, and conducting proof-ofconcept studies to assess the practical application of precision health in public healthcare. By August 2025, over 250 research projects had been funded in 19 of the country’s 27 federative units, across a range of areas, including oncological, rare, cardiovascular, infectious, neurological, and non-communicable diseases, as well as population genomics and precision health. Financial investments had exceeded BRL 1 billion, funding the sequencing of 67,000 samples. Nine large-scale genomics research projects associated with the Program have contributed to generating whole-genome data from 45,910 individuals. Moreover, four public calls have selected 209 research projects led by science and technology institutions located across all regions of Brazil. GenBR offers key lessons for LMICs seeking to implement genomics in public health, particularly in contexts marked by population diversity, infrastructure asymmetries, and fiscal constraints. Findings highlight the importance of sustained political commitment, inclusive governance, and long-term planning for building national genomic capacity and advancing health equity.
The creation of the BRICS Partnership for the Elimination of Socially Determined Diseases marks a pivotal step in positioning the social determinants of health at the forefront of global public policy and collective action. Socially determined diseases shaped by poverty, inequality, inadequate sanitation, and limited access to services, remain significant public health challenges across BRICS nations. Despite substantial progress in science, technology, and health system strengthening, global targets for disease elimination and reduction remain off track due to persistent financial gaps, fragmented programs, and insufficient multisectoral coordination. In this context, BRICS countries, representing nearly half of the world’s population, are uniquely positioned to drive transformative change by integrating health equity principles into national and international agendas. This manuscript describes the technical and political process that led to the formulation of the BRICS Partnership, culminating in its endorsement at the BRICS Leaders’ Meeting. The Partnership outlines five strategic objectives focused on strengthening resilient health systems, advancing intersectoral action, expanding research and innovation, securing sustainable financing, and aligning global positions to accelerate progress toward disease elimination. The initiative offers a comprehensive framework that addresses both disease-specific challenges and the broader structural drivers of inequity. The BRICS Partnership thus emerges as a global model of how collaboration, scientific advancement, multilateralism, and social justice can converge to accelerate the elimination, control, or reduction of socially determined diseases and promote a healthier, more equitable future.
This article analyzes the evolving health cooperation between Brazil and China as a strategic frontier in South-South collaboration. At a time of global health insecurity and technological inequality, the partnership between these two continental powers offers a transformative alternative to traditional donor-recipient models. The analysis traces a shift from commodity-based trade to a potential alliance in co-innovation, encompassing vaccines, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and digital health. Brazil’s deep dependency on imported medical inputs and its fragmented industrial base stand in contrast to China’s state-led model of technological scaling and global health outreach. Yet, this asymmetry also reveals opportunities: Brazil’s universal health system (SUS), research institutions, and regional leadership can be aligned with China’s production capacity, digital infrastructure, and development finance to build shared technological sovereignty. The paper examines how Brazil’s renewed industrial policy under Lula’s administration opens new pathways for joint R&D, regional pharmaceutical production, and equitable technology transfer. It also confronts persistent challenges—technological imbalances, intellectual property constraints, institutional volatility, and geopolitical pressures aimed at curtailing South-South alignment. A successful partnership, the article argues, must be grounded in transparent governance, mutual benefit, and a commitment to health as a public good. It concludes with a proposal for a decentralized health innovation ecosystem in Brazil, inspired by China’s special economic zones, to overcome the historical concentration of technological power and promote equitable development across the North, Northeast, and Center-West. In doing so, the Brazil-China relationship can become a model for a more just, resilient, and multipolar global health order.
This study aimed to assess the implementation of the Brazilian National Program for Genomics and Precision Public Health (GenBR) over its initial five years, identifying key achievements, challenges, and lessons for integrating genomics into public health systems in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Established by Ministerial Ordinance GM/MS No. 1,949 on August 4, 2020, GenBR aims to lay the foundation for genomics and precision health within Brazil’s Unified Health System. Its primary goals include advancing science and technology countrywide, fostering the development of a national genomics industry, and conducting proof-of-concept studies to assess the practical application of precision health in public healthcare. By August 2025, over 250 research projects had been funded in 19 of the country’s 27 federative units, across a range of areas, including oncological, rare, cardiovascular, infectious, neurological, and non-communicable diseases, as well as population genomics and precision health. Financial investments had exceeded BRL 1 billion, funding the sequencing of 67,000 samples. Nine large-scale genomics research projects associated with the Program have contributed to generating whole-genome data from 45,910 individuals. Moreover, four public calls have selected 209 research projects led by science and technology institutions located across all regions of Brazil. GenBR offers key lessons for LMICs seeking to implement genomics in public health, particularly in contexts marked by population diversity, infrastructure asymmetries, and fiscal constraints. Findings highlight the importance of sustained political commitment, inclusive governance, and long-term planning for building national genomic capacity and advancing health equity.
BRICS leaders gathered for the 17th Summit on July 6–7 in Rio de Janeiro, where they issued the Rio de Janeiro Declaration, themed “Strengthening Global South Cooperation for More Inclusive and Sustainable Governance.” Alongside the main document, three additional statements were released. In the human and social development promotion section of the main document, the health-related paragraphs highlight two initiatives led by Fiocruz, a strategic institution of the Brazilian State: the BRICS Network of Research in Public Health and Health Systems and the BRICS Vaccine Research and Development Center. The BRICS Network on Research in Public Health and Health Systems fosters health cooperation to address structural and health inequalities in the Global South. It operates on the premise that robust public health systems can drive social and economic improvements, directly and indirectly enhancing living conditions for populations. Meanwhile, the BRICS Vaccine R&D Center is a strategic instrument aimed at enabling member countries to develop autonomous solutions for preventing and controlling infectious diseases, as well as responding to public health emergencies—both domestically and in other nations in need. A third initiative, the Conference of the BRICS National Public Health Institutes (NPHIs), is also being coordinated by Fiocruz. Though not mentioned at the Leaders’ Summit, its significance earned it a place in the BRICS Health Ministers’ declaration. Its recommendations will help advance knowledge on public health issues and support decision-making processes. The BRICS Summit yielded highly positive outcomes across all fronts, though continued follow-up will be necessary to ensure the implementation of approved proposals.
The creation of the BRICS Partnership for the Elimination of Socially Determined Diseases represents a historic opportunity to place the social determinants of health at the center of public policy, particularly considering the need to advance health equity. Strategically, BRICS countries can lead a global transformation that goes beyond ensuring access to treatment for
long-standing diseases and can expand actions to address threats rooted in social, economic, and environmental factors that impact societies. This manuscript outlines the process leading to the proposal of this BRICS partnership, culminating in its endorsement at the BRICS
Leaders’ Meeting. The BRICS Partnership for the Elimination of Socially Determined Diseases stands as a global model of how collaboration, scientific advancement, multilateralism, and social justice can converge to build a healthier, more equitable future.
ISSN 3034-4719 (Online)