The BRICS are a group of leading emerging economies. Originally comprising five countries, the BRICS have now expanded to include ten countries: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, the United Arab Emirates and Indonesia.
The BRICS countries are home to 48% of the world’s population and have similar challenges in health care.
The BRICS Health Journal aims to promote medical research, public health and scientific cooperation among the BRICS countries.
In the scope of the BRICS Health Journal:
- Public health
- Health care system
- Medical education
- Infectious diseases
- Noncommunicable diseases
- Digitisation of healthcare
- The global challenge of cancer
- Mental health
- Maternal and child health
- Tuberculosis control
- Advancing the global fight against HIV/Aids
- Antimicrobial resistance
The Journal is issued four times a year and publishes original research articles, review articles and letters to the editor.
Journal target audience
- Scientists and Researchers: Medical professionals, physicians, scientists and researchers from the BRICS countries who are engaged in medical and scientific research and strive to publish their work in a ranked and recognized journal.
- Medical organizations and institutions: Medical centres, hospitals, research institutes and clinics in the BRICS countries that are interested in disseminating their scientific and clinical research.
- Health Authorities and State Institutions: Ministries of Health and other public authorities responsible for health care in the BRICS countries who can use the journal to share experience and information about health care.
- Medical schools: Students of medical and scientific specialties, graduate students and scientific teachers from medical schools of the BRICS countries.
- International organizations and partners: International scientific and medical organizations that are interested in cooperation with scientists and medical specialists from the BRICS countries
Current issue
Background: Healthcare is one of the priority sectors for the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) worldwide, including Russia. The key area of AI implementation is the integration of AI-based medical devices into the Unified Digital Framework in the healthcare sector of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The aim of this study is to analyze the development and implementation outcomes of AI in the Russian healthcare system in 2018–2024.
Materials and methods: The data regarding AI implementation were extracted from legislation, scientific publications and provided by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and the national technical committee for standardization in the AI technologies.
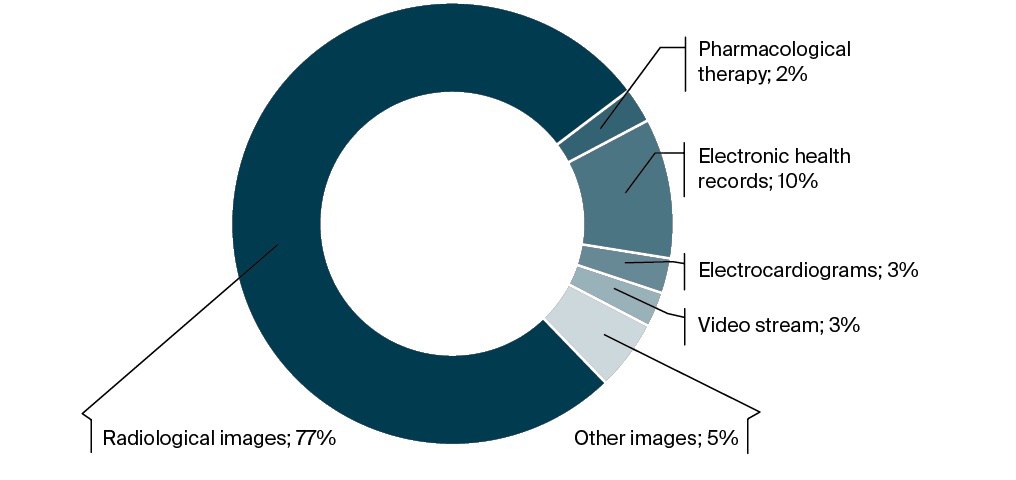
Results: In Russia, 77% of AI-based medical devices are intended for medical image analysis. Between 2018 and 2024, 69% of investments in the development and implementation of AI solutions in healthcare came from state sources. Scientific research in this field is actively progressing: research institutions under the Russian Ministry of Health are implementing 215 AI-related healthcare projects. A total of 21 national and pre-liminary technical standards in the field of AI for healthcare have been developed and approved. In 2023, the deployment of AI-based medical devices began across the Russian regions. As of 01.01.2025, a total of 412 AI-based medical devices had been implemented, of which 83% are used for image analysis and 16% for electronic health record analysis.
Conclusion: A set of measures is being developed to actively introduce AI into healthcare, including the legal frameworks, attracting investments, conducting research and developing new products.
Tuberculosis remains a major public health issue in China, with 741,000 new cases in 2023. Despite significant strides in tuberculosis control, suboptimal case detection and low acceptance rate of tuberculosis preventive treatment hamper tuberculosis elimination. To meet the WHO’s 2030 End Tuberculosis target, China’s “National Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Program (2024–2030)” prioritizes active case finding and preventive treatment. Active case finding targets high-risk groups (people living with human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, the elderly, individuals with diabetes and previously treated tuberculosis patients and close contacts of tuberculosis patients) using advanced screening methods. Implementation of active case finding should be performed in setting- ang region-specific manner. Tuberculosis preventive treatment focuses on latent tuberculosis infections with shorter, safer regimens. The effective implementation of tuberculosis preventive treatment requires integration into the comprehensive “Center for Disease Control and Prevention − Hospital − Primary Medical Institutions” framework. The “Zero-TB Communities” initiative integrates these strategies, aiming at fewer than 10 cases per 100,000 people. The framework of this initiative includes screening for active tuberculosis cases, drug resistant tuberculosis and latent tuberculosis infection, management of identified tuberculosis cases and tuberculosis preventive treatment, as long as social advocacy and mobilization. Through evidence-based interventions and multi-sector collaboration, China aims to accelerate tuberculosis control and contribute to global elimination efforts.
Introduction: The use of conventional methods of drug administration during antibiotic therapy of critically ill patients may be insufficient since the minimum inhibitory concentration required for effective therapy may not be maintained for the required amount of time due to the peculiarities of the patients’ pharmacokinetics. Endolymphatic therapy has been proposed as an alternative approach.
Aim: The evaluation of meropenem pharmacokinetics during endolymphatic antibiotic therapy and its comparison to intravenous administration route.
Materials and methods: The blood samples from patients treated with meropenem endolymphatically (n = 1) and intravenously (n = 1) were analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection and high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass-spectrometry.
Results: In intravenous and endolymphatic administration of meropenem minimum plasma concentration at steady state was 10 µg/ml and 16.39 µg/ml, maximum plasma concentration at steady state – 42.41 µg/ml and 42.57 µg/ml, area under the curve at steady state – 363.997 µg·h·ml-1 and 521.86 µg·h·ml-1, mean residence time – 8.446 and 11.365 hours.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate longer persistence of meropenem in circulation after endolymphatic administration thus indicating preferable pharmacokinetics. Additionally, minimum plasma concentration at steady state after endolymphatic treatment remained at a high level, exceeding minimum inhibitory concentration. However, further studies in larger cohorts are required for obtaining reliable confirmations of endolymphatic administration route benefits.
Egypt faces a major challenge due to its rapid population growth. The growth rate of 2.56% from 2006 to 2017 far exceeds the economic growth needed to support it. Even though life expectancy has improved and mortality rates have decreased, high birth rates remain a significant obstacle. The country’s large youth population could offer a demographic advantage. Several health-related challenges are currently faced by the country, including high out-of-pocket spending, uneven distribution of health services, and the growing burden of non-communicable diseases. Despite the challenges, the government successfully maintained several ongoing health programs, initiated multiple national projects, and achieved significant international recognition for the milestones it reached. The country also successfully implemented universal health coverage in six governorates by 2025, out of 27 Egyptian governorates. Additionally, Egypt hosted multiple international conferences that contributed to the design and implementation of global, regional, and national population and health strategies. Recently, Egypt launched its National Population Strategy (2023–2030) and National Health Strategy (2024–2030), which outline plans to mitigate the risks of overpopulation and focus on improving health and well-being. These efforts are aligned with the initiation of several public health interventions that have successfully alleviated suffering from various endemic diseases. All these initiatives are crowned by the national project for human development, paving the way for healthy, efficient, and culturally rich generations. Although fertility rates have decreased significantly, Egypt continues to aim for these reductions to align with improvements in the Human Development Index and longer life expectancy.
Background: Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) using lower gastrointestinal (GI) specimens can detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA in patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. However, the association between cycle threshold (Ct) values from such specimens and the presence of GI manifestations remains unclear.
Materials and methods: An analytical cross-sectional study was conducted using secondary, de-identified hospital records from three Indonesian medical centers (July–November 2020). Adult patients with positive lower GI RT-PCR results and available Ct values were included. Ct values were dichotomized as low (<25) or high (≥25). GI symptoms assessed included nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation. The primary outcome was the association between Ct category and the presence of any GI symptom, analyzed using Fisher’s exact test. Results are presented as prevalence ratios (PRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: A total of 37 patients met the inclusion criteria (43.2% male; mean age 44.8 ± 13.2 years). Only one patient (2.7%) exhibited a low Ct value, while 36 (97.3%) had high Ct values. Overall, 22 patients (59.5%) reported at least one GI symptom. The most frequently reported symptom was nausea (54.1%), followed by vomiting (18.9%), abdominal pain (16.2%), and diarrhea (13.5%); constipation was not observed. No significant association was found between Ct category and the presence of GI symptoms (p = 0.595; PR 1.048, 95% CI 0.956–1.148).
Conclusion: Among adults with SARS-CoV-2 detected via RT-PCR from lower GI specimens, Ct value category was not significantly associated with GI symptom presence. These findings underscore the limited prognostic value of Ct values from lower GI sampling and emphasize the need for larger, prospectively designed studies with standardized protocols.
Introduction. Healthcare is one of the priority sectors for the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies worldwide, including Russia. The key area of AI implementation is the integration of AI-based medical devices (AI MDs) into the Unified Digital Framework in the healthcare sector of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Objective. An analysis of the development and implementation outcomes of AI technologies in the Russian healthcare system in 2023–2024.
Results. In Russia, 77% of medical devices based on artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are intended for medical image analysis. Between 2018 and 2024, 69% of investments in the development and implementation of various AI solutions in healthcare came from state sources. Scientific research in this field is actively progressing: research institutions under the Russian Ministry of Health are implementing 215 AI-related healthcare projects. A total of 21 national and preliminary technical standards in the field of AI for healthcare have been developed and approved. In 2023, the deployment of AI-based medical devices began across the Russian regions. As of 01.01.2025, a total of 412 AI-based medical devices had been implemented, of which 83% are used for image analysis and 16% for electronic health record analysis.
Conclusion. Currently, a set of measures is being developed to actively introduce AI technologies into healthcare, including the development of legal frameworks, attracting investments, conducting scientific research and developing new products.
**Abstract**
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major public health issue in China, with 741,000 new cases in 2023. To meet the WHO’s 2030 End TB target, China’s "National TB Prevention and Control Program (2024–2030)" prioritizes active case finding (ACF) and preventive treatment (TPT). ACF targets high-risk groups using advanced screening methods, while TPT focuses on latent TB infections with shorter, safer regimens. The "Zero-TB Communities" initiative integrates these strategies, aiming for fewer than 10 cases per 100,000 people. Through evidence-based interventions and multi-sector collaboration, China aims to accelerate TB control and contribute to global elimination efforts.
The use of conventional methods of drug administration during antibiotic therapy of critically ill patients may be insufficient since the MIC required for effective therapy may not be maintained for the required amount of time due to the peculiarities of the patients' pharmacokinetics. Endolymphatic therapy has been proposed as an alternative approach. This article presents information on the evaluation of pharmacokinetics during endolymphatic antibiotic therapy, as well as the obtained comparative pharmacokinetic data compared to intravenous administration.
Egypt faces a major challenge due to its rapid population growth, which strains economic resources and the healthcare system. The growth rate of 2.56% from 2006 to 2017 far exceeds the economic growth needed to support it. Even though life expectancy has improved and mortality rates have decreased, high birth rates remain a significant obstacle. The country's large youth population could offer a demographic advantage, but this is offset by a rising dependency ratio. Several health-related challenges are currently faced by the country, including high out-of-pocket spending, uneven distribution of health services, and the growing burden of non-communicable diseases. Despite the challenges, the government successfully maintained several ongoing health programs, initiated multiple national projects, and achieved significant international recognition for the milestones it reached. Egypt succeeded in eliminating a series of highly devastating infectious diseases and reducing the morbidities associated with various non-communicable diseases. The country also successfully implemented universal health coverage (UHC) in six governorates by 2025, out of 27 Egyptian governorates. Additionally, Egypt hosted multiple international conferences that contributed to the design and implementation of global, regional, and national population and health strategies. Recently, Egypt launched its National Population Strategy (2023-2030) and National Health Strategy (2024-2030), which outline plans to mitigate the risks of overpopulation and focus on improving health and well-being. These efforts are aligned with the initiation of several public health interventions that have successfully alleviated suffering from various endemic diseases. All these initiatives are crowned by the national project for human development, paving the way for healthy, efficient, and culturally rich generations. Although fertility rates have decreased significantly, Egypt continues to aim for these reductions to align with improvements in the Human Development Index and longer life expectancy.
Background: Anal swab RT‑PCR can detect SARS‑CoV‑2 RNA in patients with gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms, yet how cycle threshold (Ct) values from anal swabs relate to GI manifestations remains unclear. Methods: We performed an analytical cross‑sectional study using secondary, de‑identified hospital records from three Indonesian centers (July–November 2020). Adults with positive RT‑PCR from anal swabs and available Ct values were included. Ct values were categorized as low (<25) vs high (≥25). GI symptoms recorded were nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation. The primary outcome was the association between Ct category and presence of GI symptoms, analyzed using Fisher’s exact test with prevalence ratio (PR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). Results: Thirty‑seven patients met inclusion criteria (43.2% men; mean age 44.8±13.2 years). One patient (2.7%) had low Ct and 36 (97.3%) had high Ct. Overall, 22/37 (59.5%) had ≥1 GI symptom; the most frequent was nausea (54.1%), followed by vomiting (18.9%), abdominal pain (16.2%), and diarrhea (13.5%); no constipation was recorded. There was no significant association between Ct category and GI symptoms (p=0.595; PR 1.048, 95% CI 0.956–1.148). Conclusions: Among adults with positive anal swab RT‑PCR, Ct category did not correlate with GI symptom presence. These null findings suggest that Ct values from anal swabs should be interpreted cautiously for symptom prognostication and underscore the need for larger, prospectively collected datasets.
ISSN 3034-4719 (Online)